Example: Predicting the location of an object undergoing constant force motion
The fan cart in the video below is observed to accelerate uniformly to the right. The air exerts a constant force on the blades that is around 0.45N. Determine the how far the fan cart has traveled after 2.2s if the cart starts from rest.
Facts
- The fan cart accelerates uniformly to the right.
- The force by the air on the blades if 0.45N.
- The fan cart travels to the right for 2.2s.
- The fan cart starts from rest.
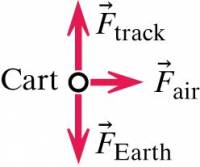
- The fan cart experiences several forces including:
- the force of the air on the blades (to the right)
- the gravitational force due to the interaction with the Earth (directly downward)
- the force applied by the track (directly upward)
- a frictional forces and air resistance that resist the motion
- The acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 ms2 and is directed downward.
Lacking
- The mass of the fan cart is not given, but can be found online (mcart=0.3kg).
Approximations & Assumptions
- Over the interval that we care about it, we will assume the net force doesn't change. That is, the cart experiences constant force motion.
- As a result, the motion occurs only in the horizontal direction.
Representations
- The forces acting on the fan cart (the system's interactions with its surroundings) are represented in this free-body diagram.
- The net force acting on the fan cart is the sum of all the forces, →Fnet=∑→Fi=⟨0.45,0,0⟩N.
- The displacement of the fan cart in the x-direction can be written like this: xf−xi=vxiΔt+12Fnet,xmΔt2
Solution
The displacement of the cart is given by,
Δxcart=xcart,f−xcart,i=vcart,xiΔt+12Fnet,xmcartΔt2
We can compute this displacement,
Δxcart=(0ms)(2.2s)+120.45N0.3kg(2.2s)2=3.6m