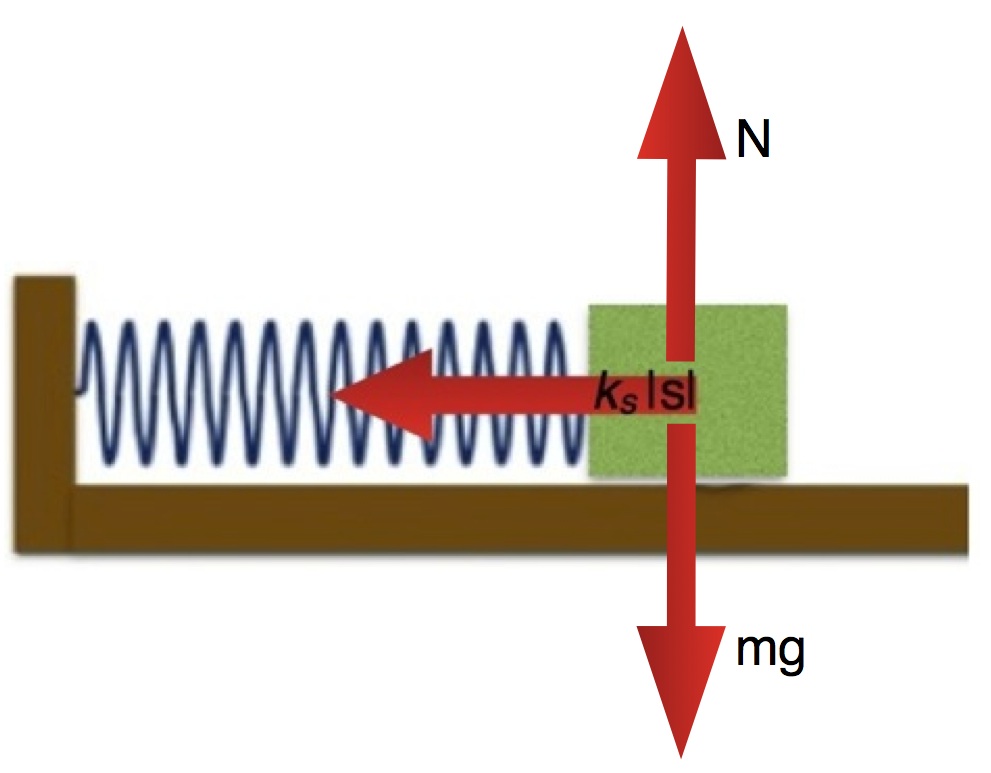
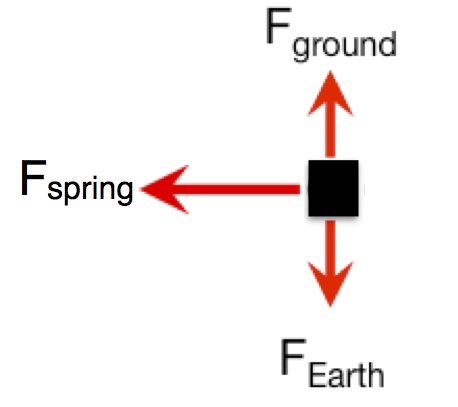
Example: Calculating the force due to a stretched spring
A spring with a mass block at the end of it and with a stiffness of 8 $N/m$ and a relaxed length of 20 $cm$ is attached to a chamber wall that results in its oscillations being horizontal. At a particular time the location of the block mass is $\langle .38,0,0 \rangle\,m$ relative to an origin point where the spring is attached to the chamber wall. Determine the force exerted by the spring on the mass at this instant.
Facts
- Spring has relaxed length of 0.2m, $L_0=0.2\,m$
- Spring has spring constant of $8 N/m$, $k_s=8\,N/m$
- At the moment of interest, the mass block is at position $\vec{L} = \langle .38,0,0 \rangle m$
- The net force acting on system is due to spring force (the gravitational force exerted by the Earth has the same magnitude as the force exerted by the horizontal surface)
Lacking
- The force that the spring exerts
Approximations & Assumptions
- Origin is at chamber wall $\langle 0,0,0 \rangle\,m$
- Assume no forces due to drag or to friction
Representations
Solution
To determine the spring force, you will need to compute: $$ {\vec F_{spring}} = -k_s\vec{s} = -k_s|\vec{s}|\hat{s}$$
You will start be determining the position vector ($\vec{L}$) of the mass and the length of the position vector ($|\vec{L}|$), $$\vec{L} = \langle 0.38,0,0 \rangle m - \langle 0,0,0 \rangle m = \langle 0.38,0,0 \rangle m$$
$$|\vec{L}| = 0.38m$$
These can be used to compute the unit (direction) vector for the stretch ($\hat{s}$), which is in the same direction as the position vector: $$\hat{s} = \hat{L} = \dfrac{\langle 0.38,0,0\rangle}{0.38} = \langle 1,0,0 \rangle$$
You can then compute the magnitude of the stretch $(|\vec{s}|)$: $$ |\vec{s}| = |L - L_0| = 0.38m - 0.20m = 0.18m$$
Finally, you can compute the force:
$$\vec{F} = -k_s|\vec{s}|\hat{s} = -(8N/m)(0.18m)\langle 1,0,0\rangle = \langle -1.44,0,0 \rangle\,N$$
which points to the left. That is consistent with the diagram above.